97.4.-HYDATID CYSTS IN SOUTHWEST OF SPAIN. A FORENSIC POINT OF VIEW. HISTOPATHOLOGICAL FINDINGS IN LUNGS AND LIVER.
Prof.Garfia.A
97.4-HIDATIDOSIS Patologia FORENSICS EN EN EL SURO DE ESPAÑA: HALLAZGOS Pulmonary Y HEPÁTICOS.
Prof.Garfia.A
97.4-hydatidosis IN FORENSIC PATHOLOGY IN SOUTHWEST SPAIN : PATHOLOGICAL FINDINGS IN LIVER AND LUNG.
Prof.Garfia.A
CASE No. 4
personal history
Patient 65, who has a history of allergy to the "straw." Smoker until a few years ago. Malta has experienced fever. Suffering from COPD and hypertension blood laying in drug treatment. He was referred to the Service of Digestive Surgery, from Internal Medicine, where he was examined and diagnosed with liver hydatid cyst of 20 cm plant diámetro.Fue admitted to undergo elective surgery.
Physical
Obesity. Normal color of skin and mucous membranes.
AP: decreased breath sounds in the right lung base. AC: No changes.
Investigations
Analysis: Leukocytes: 7,500 (Seg.64; Lin. 20; Mon.7; Eo.6; Bas.0.6). Hb: 15.8, Ht: 48.6; VCM : 90.2; HCCM: 32.5; PLQ. 226,000.
INR: 1.01, prothrombin time: 99%; T. cephalin: 40.2, fibrinogen: 393.
Glu: 107; Urea: 56; uric acid: 8.3, Albumin 4.4, Total Protein: 8.2, Creatinine: 1.22, LDH: 291; Amylase: 45, GOT: 21; GPT: 20; F.alcalina : 310; Bil.total: 0.58; Bil. Direct: 0.19; Cholinesterase: 11941, Cholesterol 231, Triglycerides: 113, Ca: 9.78, Na: 141, K: 4.5.
HBs Ag and HCV Ab: negative.
hydatidosis Serology: positive (1 / 400).
Rx Chest right hemidiaphragm elevation.
Rx abdomen Hepatomegaly .
.- Surgical Intervention
was conducted bilateral subcostal laparotomy, extended to last right intercostal space. Hydatid cyst is discovered that measures 25x20 cm. Occupies the entire right lobe and presents intimate and firm adhesion to the diaphragm, retroperitoneum, inferior vena cava, from the upper renal pole to the diaphragmatic hiatus, moved to the gallbladder and covers the posterior capsule-in-a right hepatic veins, which are linked to empties into the inferior vena cava. It makes quistoperiquistectomía closed after ligation of vascular structures and bile, cholecystectomy and resection of tongue remnant of the right lobe liver. It left two silicone drains subdiafragmático.Hemostasis satisfactoria.Cierre liver cell layers.
Fig. 1. - abdominal ultrasound.
was reported by the radiologists as compatible with hepatic hydatid cyst 20 cm in diameter.
FIG.2. -
Fig. 3 .-
.- Surgical Intervention
Fig .4 .- cyst or cupa entire right lobe and has adhesions, intimate and firm, diaphragm, retroperitoneum, inferior vena cava, from the upper renal pole to the diaphragmatic hiatus, moved to the gallbladder biliary and the posterior includes, in its capsule-a right hepatic veins, which are linked to the opening in the inferior vena cava.
CASE No. 4
personal history
Patient 65, who has a history of allergy to the "straw." Smoker until a few years ago. Malta has experienced fever. Suffering from COPD and hypertension blood laying in drug treatment. He was referred to the Service of Digestive Surgery, from Internal Medicine, where he was examined and diagnosed with liver hydatid cyst of 20 cm plant diámetro.Fue admitted to undergo elective surgery.
Physical
Obesity. Normal color of skin and mucous membranes.
AP: decreased breath sounds in the right lung base. AC: No changes.
Investigations
Analysis: Leukocytes: 7,500 (Seg.64; Lin. 20; Mon.7; Eo.6; Bas.0.6). Hb: 15.8, Ht: 48.6; VCM : 90.2; HCCM: 32.5; PLQ. 226,000.
INR: 1.01, prothrombin time: 99%; T. cephalin: 40.2, fibrinogen: 393.
Glu: 107; Urea: 56; uric acid: 8.3, Albumin 4.4, Total Protein: 8.2, Creatinine: 1.22, LDH: 291; Amylase: 45, GOT: 21; GPT: 20; F.alcalina : 310; Bil.total: 0.58; Bil. Direct: 0.19; Cholinesterase: 11941, Cholesterol 231, Triglycerides: 113, Ca: 9.78, Na: 141, K: 4.5.
HBs Ag and HCV Ab: negative.
hydatidosis Serology: positive (1 / 400).
Rx Chest right hemidiaphragm elevation.
Rx abdomen Hepatomegaly .
.- Surgical Intervention
was conducted bilateral subcostal laparotomy, extended to last right intercostal space. Hydatid cyst is discovered that measures 25x20 cm. Occupies the entire right lobe and presents intimate and firm adhesion to the diaphragm, retroperitoneum, inferior vena cava, from the upper renal pole to the diaphragmatic hiatus, moved to the gallbladder and covers the posterior capsule-in-a right hepatic veins, which are linked to empties into the inferior vena cava. It makes quistoperiquistectomía closed after ligation of vascular structures and bile, cholecystectomy and resection of tongue remnant of the right lobe liver. It left two silicone drains subdiafragmático.Hemostasis satisfactoria.Cierre liver cell layers.
Fig. 1. - abdominal ultrasound.
was reported by the radiologists as compatible with hepatic hydatid cyst 20 cm in diameter.
FIG.2. -
abdominal CT. Report.
right hepatic lobe atrophy secondary to the presence of a cystic lesion measuring 21x16x20 cm. The lesion has a uniform capsule, with some punctate calcification therein. Inside the lesion is small objectify linear images that could correspond to membranes. After contrast administration, no evidence of uptake within it. The lesion is suggestive of hydatid cyst and is in contact with hepatic veins and intrahepatic segment of the inferior vena cava. In the remaining parenchymal focal no lesions. Normal-sized bile ducts. Spleen, pancreas and splenoportal axis, no pathological findings. Normal kidneys.
right hepatic lobe atrophy secondary to the presence of a cystic lesion measuring 21x16x20 cm. The lesion has a uniform capsule, with some punctate calcification therein. Inside the lesion is small objectify linear images that could correspond to membranes. After contrast administration, no evidence of uptake within it. The lesion is suggestive of hydatid cyst and is in contact with hepatic veins and intrahepatic segment of the inferior vena cava. In the remaining parenchymal focal no lesions. Normal-sized bile ducts. Spleen, pancreas and splenoportal axis, no pathological findings. Normal kidneys.
Fig. 3 .-
.- Surgical Intervention
It held a bilateral subcostal laparotomy, extended to last right intercostal space. Hydatid cyst is discovered that measures 25x20 cm.
Fig.5 .- closed quistoperiquistectomía is performed after ligation of vascular structures and bile Tongue cholecystectomy and resection of the right lobe liver remaining. It left two silicone drains and subdiaphragmatic liver cell. Hemostasis satisfactoria.Cierre layers.
POST .-
Postoperatively, the patient has hypotension, severe bradycardia, and subsequent cardiac arrest. It began cardiopulmonary resuscitation associated with cardioactive drugs. The patient left the unemployment supraventricular tachycardia that was treated medically with pressors and oxygen saturation. Presents new bradycardia and subsequent cardiac arrest. Restarted resuscitation without success.
was performed an autopsy familiar legal malpractice complaint.
HISTOPATHOLOGY
1 .- .- Macroscopic description
HISTOPATHOLOGY
1 .- .- Macroscopic description
; Macroscopically it was a giant cyst formation, spherical, 5 kg of weight, measuring 24 cm in diameter after fixation in formalin. The outer cyst surface had yellowish brown color, cut, cautioned a single cavity completely occupied by gelatinous material, yellowish-white, within which identified a laminar formation, blackish brown, friable and necrotic, 0.3 cm thick and 15 cm in length. The cyst wall had firm, whitish and about 1 cm thick, on the inside of the capsule could distinguish some areas of thickening and sinuous surface, the largest of which measured 3.2x3cm. In the serial sections, these areas had the same macroscopic appearance as the rest of the wall.
Fig.6 .- Hemisection cyst after fixation in formalin. Note that the content is gelled and within it remains of human membranous-looking serpent-trapped in the gelatinous mass. Prof.Garfia.A
FIG.7 .- Note the presence of lamellar bodies within the cyst Images TAC. Prof. Garfia.A
Details Fig.8.-detached laminar membrane, within the gelatinous mass.
Frider B. et al. (Newsletter of hydatidosis, No. 15. 1997.Asociación Hidatología International), have considered that hydatid cysts may be modified, the images obtained by ultrasound, aging support them. Described 7 types of cysts which ultrasonographic description -according to the biological evolution of hydatid cyst- corresponds to the following morphological types:
I. - Hyaline.
II .- Hyaline with daughter cysts.
III. -multilocular.
IV .- with membrane peeling.
V. - Heterogeneous partial with or without calcification.
VI .- Solid, with or without partial calcification.
VII .- Calcified.
This giant cyst presents evolutionary biology for Groups IV and VI (solid and membrane peeling: dead cyst), taking into account the proviso in question here, and no ultrasonic tomographic images.
.- 2.-Microscopic description
Cyst wall or adventitia (ad) and is comprised of a sheath of dense connective tissue which can be seen, out, few inflammatory foci composed of eosinophil leukocytes and lymphocytes. On the inside of the wall are noted numerous multinucleated giant cells, arranged around the remains of layered membranes consisting of acellular hyaline material (hyaline membranes), in many of the giant cells are found remains laminar intracellular phagocytosed. Prof.Garfia.A
Fig.9 .- panorama stitching, a small increase of the cyst wall to show the adventitia (ad), the absence of germ layer, and the shedding of the membrane sheet (arrows) into the cystic cavity (with).
Prof. Garfia.A
Photographs 1 to 6, which follow, are a series taken at 400 magnification of the inside of the cyst wall in the area corresponding to the location laminated membrane, just inside the adventitia.
Fig 10 .- Series: Photo 1 .-
; It appears that the cystic cover - laminated and germinal layers, have been replaced by an "inflammatory neocapa" multinucleated giant cells that are "almost a multinucleate syncytium. Arrows pointing both laminar fragments engulfed by giant cells (Ad = adventitia). Prof.Garfia.A
Fig 11.-Series: Photo 2
The arrow pointing membrane remains laminar phagocytosed. Prof.Garfia.A
Fig 12.-Series: Photo 3 .-
" Pool "of giant cells have numerous cytoplasmic inclusions phagocytosed.
Prof.Garfia.A
Fig 13.-Series: Photo 4
The arrow pointing to the phagocytosis of a large piece of membrane by the combined action of several giant cells (Ad = adventitia).
Prof.Garfia.A
Fig.14.-Series: Photo 5
Right photograph No. 4. Detail of the "neocapa."
Prof.Garfia.A
Fig.15 .- Series: Photo 6 .- From the adventitia cystic fibrous layer (d) into the cyst, it appears that cystic covers have disappeared-or chitinous laminar layer detached within the cystic cavity, and the germinative layer have been replaced by an "inflammatory neocapa" , consisting of epithelioid cells and numerous multinucleated giant cells that include remnants laminated membrane. Prof. Garfia.A
Fig. 16 .- The chitinous material laminated cover awakens an inflammatory response of such magnitude, that between the adventitial fibrous layer and the laminate is organized almost a true syncytial layer multinucleated giant cells, as shown in the picture. Prof.Garfia.A
Fig. 17 .- Together with cystic adventitial sheet , a constituent of the thick laminated chitinous membrane, is being swallowed up by several multinucleated giant cells, at both ends. Prof.Garfia.A
Fig 19.-Detail of one of scolices dead, in the previous figure (s). Prof. Garfia.A
Fig.20 .- This photograph and the next two show different increases in the activity of a giant cell in the process of phagocytosis of a laminated membrane remaining. Prof.Garfia.A
Fig.22 .- Note the arrangement of the cell nuclei, giant cell, in two rows separated by a wide band of cytoplasm. Prof.Garfia.A
Fig. 23 .- To the right of the image are found fragments of laminated membrane, stained blue, included in amorphous material that stains intensely red. Next to the remains is a polymorphonuclear leukocyte infiltrate. Prof. Garfia.A
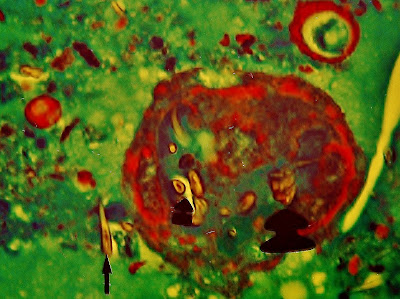
Fig.24 .- The arrows indicate the presence of typical corona hooks - which is located at the head of scolices-floating freely within the cyst, from scolices dead. Prof. Garfia.A
Fig. 25 .- The figure seems to correspond to the necrotic ghost of a daughter vesicle containing several scolices, which come from the numerous hooks contained in it (thick arrows). Outside of the gallbladder found floating in the magma hooks gel that fills the cyst. Note the appearance of hooks in cross section and the recess in its interior hook small arrowed. Prof.Garfia.A
Thanks .-
I am deeply grateful to Dr. Angel Prado Morales, Chief of General Surgery Hospital Ciudad de Coria, Coria City (Cáceres), for the invaluable assistance provided for the preparation of this case.
Bibliography
JI González Muñoz et al .- giant splenic hydatid cyst.
Cir Esp 2006; 79. nº 2.
























0 comments:
Post a Comment